Science Intersects Religion
For years, we've heard about the focus of spirituality in religion and how it can have some significant mental health implications. However, we don't often discuss any of the religious traditions that may offer physical health benefits as well. Your overall health depends on the synergy of both your emotional and physical health. Let's take a look at just a few of the religious traditions that have clinically proven health benefits.
Fasting
Fasting or abstaining from food, drink, or both, may seem like the most popular weight-loss fad, but the practice dates back thousands of years to religions and religious purposes.
Ancient Fasting
Ancient civilizations fasted to prepare priests and priestesses to approach the deities who were thought to only reveal themselves and their divine teachings in dreams and visions after a fast by devotees. Similarly, some Native American tribes believed fasting should be practiced before a vision quest. The Pueblo Indians of the American Southwest also fasted before ceremonies connected with seasonal changes and during retreats.
Ancient Peruvians fasted for penance after an individual confessed their sins before a priest.
The Evolution of Fasting
Fasting is a characteristic of many significant religions from around the world.
Jainism
In this religion, individuals fasted according to specific rules. They believed that fasting paired with certain types of meditation lead to trances that enabled them to dissociate from their surroundings and reach a new, transcendent state of mind and body.
Buddhist monks of the Theravada school fast, too. They do this as part of their meditation practices. In India, Hindu sadhus, also known as holy men, are admired for their fasting.
Western Religions and Fasting
Judaism developed many dietary laws and customs, including the observation of many annual fast days. These take place primarily on days of repentance, such as Yom Kippur.
Christianity, and especially Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy, observes a 40-day fasting period, also known as Lent. It's a spring period of penitence that happens before Easter and during Advent, before Christmas.
Islam
In Islam, the month of Ramadan is a period of penance and requires complete fasting from morning until night.
Health Benefits of Fasting
While you may have heard of intermittent fasting, the popular weight-loss fad, there are actually many health benefits to the ancient religious tradition.
Weight Loss
We'll start with the most obvious first. Many people are finding that they can lose weight through intermittent fasting. Fasting aids weightless by limiting calorie intake and boosting metabolism. Research suggests that short-term fasting could potentially increase metabolism by increasing levels of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, also helping to enhance weight loss.1
Promotes Blood Sugar Control
Fasting may improve blood sugar control by reducing insulin resistance, as several studies have suggested. One study, in particular, involving ten people with type 2 diabetes showed that short-term intermittent fasting significantly decreased blood sugar levels. 2
By reducing insulin resistance, you can increase your body's sensitivity to insulin, which allows it to transport glucose from the bloodstream to your cells more efficiently.
Another study found that fasting is as effective as a limited calorie intake at reducing insulin resistance. 3
1 (n.d.). Resting energy expenditure in short-term starvation is increased - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10837292
2 (2017, April 15). Effects of intermittent fasting on health markers in those with ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5394735/
3 (2019, June 12). Intermittent fasting vs daily calorie restriction for type 2 ... - NCBI - NIH. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24993615
Fights Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a normal immune process that helps to fight off infections, while chronic inflammation can actually have serious health implications. Inflammation is suggested to be involved in the development of chronic conditions like heart disease, cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Fasting can help decrease levels of inflammation to promote overall health.
One study of 50 healthy adults demonstrated that intermittent fasting for one month significantly decreased levels of inflammatory markers. 4
Enhance Heart Health
Heart disease is the leading cause of death around the world, but you can reduce your risk of heart disease by making changes to your diet and lifestyle. Some research suggests that incorporating fasting into your lifestyle and dietary changes may enhance heart health as it improves blood pressure, triglycerides, and even cholesterol levels.
One such study of 110 obese adults demonstrated that fasting for three weeks under medical supervision decreased blood pressure, levels of triglycerides, and total cholesterol, including "bad" LDL cholesterol.5
Boost Brain Function
Several animal studies have found that fasting could positively affect brain health by increasing nerve cell synthesis and providing protection from neurodegenerative disorders.
Animal studies have reported that fasting can potentially increase the generation of nerve cells to enhance cognitive function. 6
As you have learned, fasting may help relieve inflammation. Because of this, fasting could also help prevent neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease, according to animal studies.
4 (2018, October 4). Intermittent fasting during Ramadan attenuates ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23244540
5 (n.d.). [The effects of three-week fasting diet on blood pressure, lipid ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17929537
6 (n.d.). Dietary restriction increases the number of newly generated ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11220789
7 Fasting may also be able to protect the brain from damage due to strokes, as one study suggests.
Circumcision
The first time circumcision was recorded was the Biblical account of Abraham. However, it is actually a far older practice originating in eastern Africa. While it may be impossible to know its true origins, one theory postulates that circumcision began as a means of purification to reduce sexuality and sexual pleasure, which was seen as impure in some ancient societies. Removal of the foreskin may also be seen as a sacrifice of sinful human enjoyment for the sake of holiness in the afterlife.
One of the oldest religious rites, Judaism took on this practice and called it B'rit milah (Covenant of circumcision). It's also referred to as a bris. This sacred ritual welcomes male babies into the Jewish community. Tradition states that it is a parent's obligation to circumcise a son and offer a threefold blessing for the child:
- A life enriched by the Torah
- The wedding canopy (chuppah)
- Good deeds
The Health Benefits of Circumcision
While the religious practice of circumcision aims to honor religion, scientists in recent years have found that it can have many health benefits in this life.
Reduced Risk of HIV (and other STIs)
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) stated that circumcision of all newborn American males might reduce the risk of getting HIV by over 15%.
Circumcision also reduces the risk of getting the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer in women and circumcision contributes at least a little in the prevention of cervical cancer in women. 8
7 (n.d.). Age and Energy Intake Interact to Modify Cell Stress ... - NCBI - NIH. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from
8 (2012, May 6). Cervical Cancer Screening: The Key to Prevention - Stop Cancer Fund. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from http://stopcancerfund.org/p-cervical-cancer-hpv/cervical-cancer-screening-the-key-to-prevention/
Additionally, they concluded that circumcision might provide protection against syphilis. More research is needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Researchers believe that the foreskin may be particularly susceptible to microscopic cuts during sexual intercourse, which may be why circumcision can help prevent these sexually transmitted infections. Microscopic wounds allow more disease-causing pathogens to enter the body, and the foreskin may trap these viruses and bacteria to provide more time for the infection to happen.
Penile Cancer
Circumcision may reduce the risk of penile cancer. However, researchers are unable to figure out why. HPV contributes to the risk for this type of cancer, so they believe this could be the reason. Penile cancer is rare in the United States, making them believe that circumcision might be the reason why.
UTI's
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) UTI's are common in the United States. Did you know? Most UTIs in males happen during the first year of their life. These infections can lead to hospitalization and invasive procedures in babies. However, circumcision reduced the risk of these infections.
Abstaining from Pork
Pork abstention is typically associated with Judaism. However, other ancient civilizations have abstained from pork as a result of their religious beliefs.
Ancient Syria
Swine were prohibited in ancient Syria and Phoenicia, and the pig and its flesh represented a taboo observed. A lost poem of Hermesianax, reported centuries later by the traveler Pausanias, reported an etiological myth of Attis destroyed by a supernatural boar to account for the fact that "in consequence of these events the Galatians who inhabit Pessinus do not touch pork."
Judaism and Islam
Concerning Abrahamic religions, clear restrictions exist in Jewish dietary laws (Kashrut) and in Islamic dietary laws (Halal).
The prohibition of certain foods is also linked to Islamic Cosmology. Accordingly, good and evil qualities are transferred by eating an object carrying a certain quality that also affects the soul of a human, the pig rendered with evil qualities.
Christianity
Although Christianity is also an Abrahamic religion, most of its adherents are permitted to consume pork. However, Seventh-day Adventists consider pork taboo, along with other foods forbidden by Jewish law. The Eritrean Orthodox Church and the Ethiopian Orthodox Church[5] do not permit pork consumption.
The Benefits of Abstaining from Pork
While some religions do now permit the consumption of pork, it is still the most commonly consumed meat in the world. Unfortunately, recent evidence has been found proving that pork may also be one of the most dangerous meats to consume, making abstaining from pork not only a religious choice but a healthy one.
Hepatitis E
Many people eat pork from head to tail, meaning they'll eat just about any part of the animal, including its liver. What many people don't know is that pork liver is the top food-based transmitter of hepatitis E.
Believe it or not, one in ten store-bought pig livers tests positive for hepatitis E in America.
Hepatitis E is a virus that infects about 20 million people every year and can lead to fever, fatigue, jaundice, vomiting, joint pain, and stomach pain, enlarged liver, and sometimes, liver failure and death. In some rare cases, this virus can lead to myocarditis, an inflammatory heart disease.
Luckily, high cooking temps can be effective in destroying the virus.
9 (2019, July 8). Hepatitis E - World Health Organization. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e
Multiple Sclerosis
This autoimmune condition involves the central nervous system. It is one of the most surprising and strange consequences that can come from eating pork. The causative role of pork in MS is not a closed case, and more research is required.
The link to MS and pork consumption has been known since the 1980s. Researchers analyzed the relationship between per capita pork consumption and MS across countries. They found that pork-averse nations like Israel and India were spared from MS, while more liberal consumers, like Denmark and Germany, faced high rates. 10
Pig brains can trigger autoimmunity as well. Between 2007 and 2009, 24 pork plant workers fell ill with progressive inflammatory neuropathy, which is characterized by MS-similar symptoms: fatigue, numbness, tingling, and pain. It was found that pig brain mist, particles of brain tissue that were blasted into the air during carcass processing, resulted in these illnesses. 11
Liver Cancer and Cirrhosis
We have known that pork consumption echoes liver cancer and cirrhosis for decades. In analyses across the globe, a study found the correlation between pork and cirrhosis mortality. Beef, however, remained liver-neutral or protective in these studies. 12
A 1985 study also found that pork intake correlated with hepatocellular carcinoma deaths as strongly as alcohol did, as liver cirrhosis is often a prelude to cancer 13
While more research is needed, it has been suggested that nitrosamines, carcinogenic compounds created when nitrates and nitrites react with certain amines from protein, particularly in high heat.
10 (n.d.). Multiple sclerosis, latitude and dietary fat: is pork the missing ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3638477
11 (n.d.). Auto-immune polyradiculoneuropathy and a novel IgG ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21696495
12 (2009, September 10). Relationship between Dietary Beef, Fat, and Pork and ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2760419/
13 (n.d.). Hepatocellular carcinoma. Relationship to wine and pork ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2996744
Yersinia
Yersiniosis, caused by Yersinia bacteria, causes 35 deaths and almost 117,000 cases of food poisoning every year in the US. Yersiniosis is frequently caused by undercooked pork consumption, and victims face a 47-times higher risk of reactive arthritis, an inflammatory joint disease triggered by infection.
While reactive arthritis usually subsides over time, Yersinia victims have a higher risk of chronic joint problems, like rheumatoid arthritis. 14
A yersinia infection could potentially raise the risk of Graves' disease15, an autoimmune condition characterized by excessive thyroid hormone production.
According to a Consumer Reports analysis, the majority of pork products (69% of tested samples) are contaminated with Yersinia bacteria 16. Proper cooking with an internal temperature of at least 145°F for whole pork and 160°F for ground pork is necessary to destroy the bacteria.
Tefillin
Judaism
Tefillin are black leather boxes which contain Hebrew scrolls. A set includes two, one for the head and one for the arm. Each consists of the scriptures, the box, and a strap. The Torah (Old Testament) tells Jewish men to bind tefillin onto their head and upper arm every weekday, and doing so is a powerful mitzvah (good deed). Religious Jewish males over the age of bar mitzvah, or thirteen years old, traditionally perform this mitzvah.
When wearing tefillin, the arm tefillin is put on first on the upper part of the weaker arm. A blessing is then recited, and then the leather strap is wrapped around the arm seven times. Next, the head tefillin is loosely fastened on the head above a person’s hairline. A blessing is then recited, and the strap is adjusted at the back of the head.
14 (2010, July 8). and Long-term Effects of Bacterial Gastrointestinal Infections - CDC. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/14/1/07-0524_article
15 (2008, February 18). Too early to dismiss Yersinia enterocolitica infection in the ... - NCBI. Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18284638
16 (n.d.). Consumer Reports Investigation of Pork Products Finds Potentially .... Retrieved July 24, 2019, from https://www.consumerreports.org/media-room/press-releases/2012/11/my-entry-4/
Benefits of Tefillin
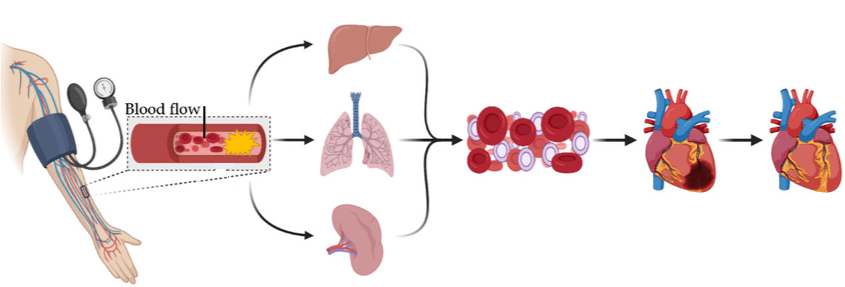
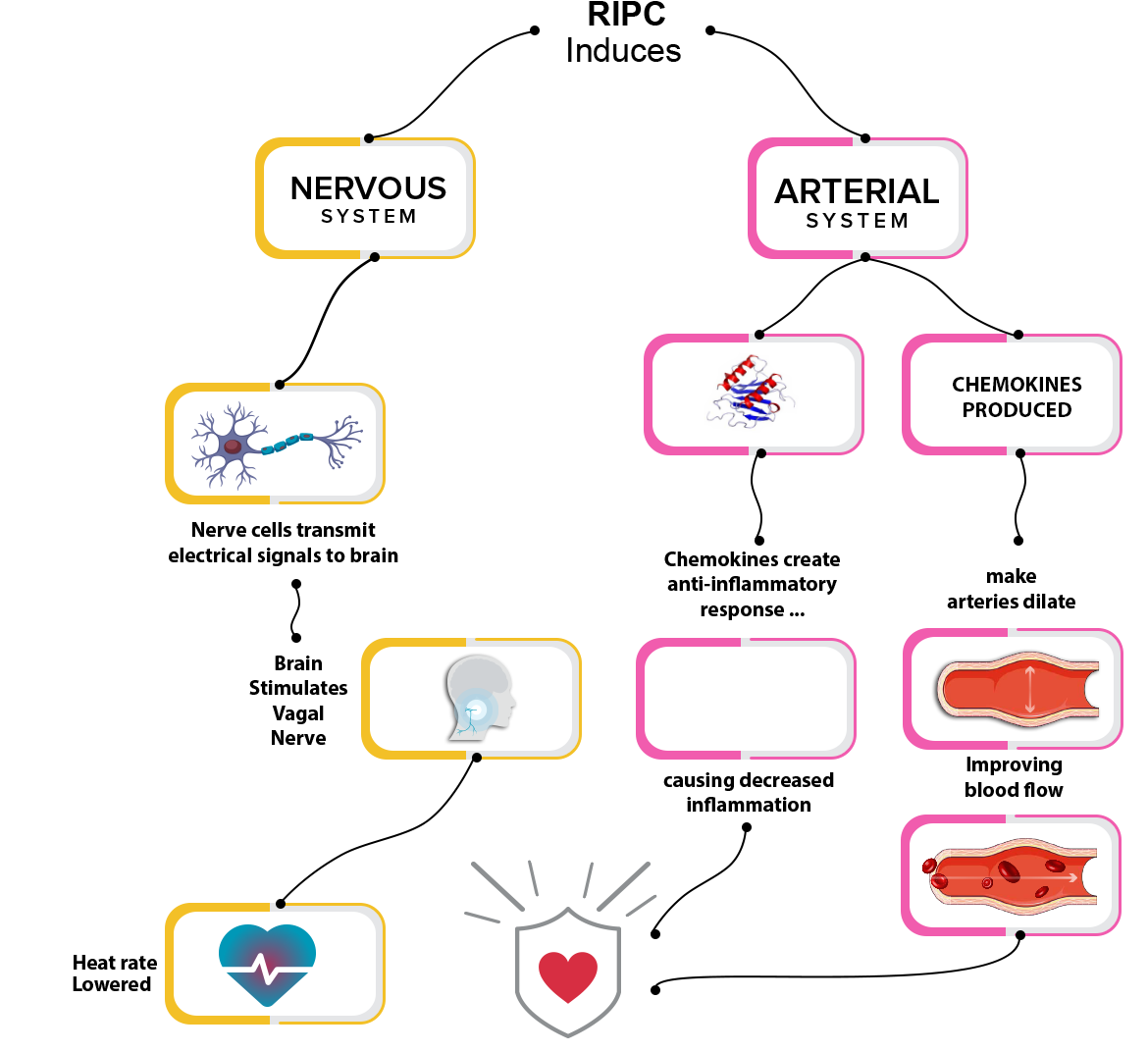
The strap wrapped tightly around the arm induces a Remote Ischemic Preconditioning (RIPC) response. RIPC occurs when blood flow to a limb is restricted and can protect other organs from a subsequent event of lack of blood flow.
Heart
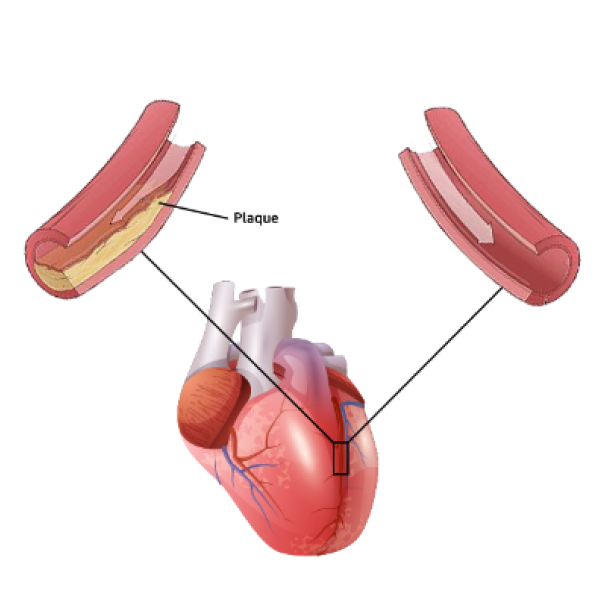
Every year, around 735,000 people suffer from a heart attack. A heart attack comes in two stages. The first stage is ischemic injury, which is when blood flow through an artery is blocked, causing a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the heart. The second stage is reperfusion injury, which is when the blood rushes back through a freshly opened artery and to the heart. Both stages can be detrimental for the vital organ
Dr. Dr. Rubinstein recently conducted a study that demonstrated how RIPC, such as that occurring from tefillin use, could prepare the vascular system for a cardiac event, like a heart attack. It also diminishes the inflammatory response and potentially prepares the immune system by downregulating chemokines that can result in reperfusion injury. Dr. Rubinstein’s study showed that RIPC might be able to precondition the heart and act as a stimulus before ischemia occurs and reduce the damage to the heart following a heart attack.
Brain and Stroke
Ischemia-Reperfusion injury is also a common feature of ischemic stroke. This occurs when blood supply is restored after ischemia. Despite the beneficial effect of the restored oxygen supply, it can also cause harm to the brain.
Dr. Yi Yang recently conducted a study to establish whether RIPC can prevent neurological diseases like stroke and reduce the damage to the brain following a stroke, or ischemia-reperfusion injury. The study monitored 50 subjects twice for 24 hours, first without preconditioning. The second time, the subjects were monitored with preconditioning using blood pressure cuffs wrapped around one upper arm and one thigh.
The results were that participants had better brain blood flow regulation 6 hours after preconditioning until 24 hours when the effect wore off. They also found an increase in the biomarker glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, which has been shown to protect against multiple nerve-related diseases. The study concluded that RIPC might help prevent neurological diseases and potentially reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury of the brain.
With all that we know about the human body, it's essential to explore the traditions of our ancestors. How is it possible that these traditions from thousands of years ago can have such a significant impact on our health? Did they know something we don’t?